Active and Passive Transducer
ACTIVE TRANSDUCER
What is meant by Active Transducer?
Active transducer is defined as transducer that does not requires an external energy source. In this type of transducer, the non-electrical quantity which is to be measured is converted to electrical output without any external source. As it does not require any external source this type of transducer is also known as a self-generating transducer.
Examples of an Active Transducer: Thermocouple, Piezoelectric Pick up & Photovoltaic.
Block Diagram of Active Transducer
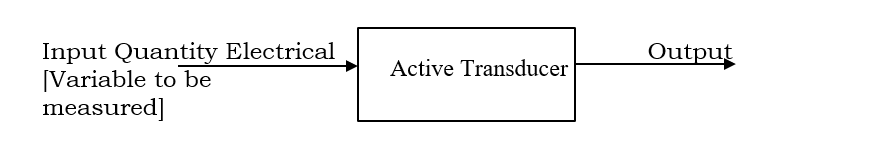
The block diagram of an active transducer is shown above. Pressure, temperature, vibration, heat radiation and flow are the various input variable that can be directly converted into electrical output.
Why active transducer is called as self-generating Transducer?
The transducer is a device that converts one form of non-electrical signal into a corresponding electrical signal. The active transducer generates electrical output directly in response to stimulation
Active transducer Classification

Active transducer is classified based on the internal physical property of the transducer. They are
listed below.
- Thermoelectric based active transducer
- Piezoelectric based active transducer
- Photovoltaic based active transducer
- Electromagnetic based active transducer
- Chemical based active transducer
List of Active transducers with its principle.
| Active Transducer | Parameter to measure | Principle |
| Thermocouple | Temperature | It works in the principle of the Seeback effect. An emf is generated when the junctions of two dissimilar metals have a change in temperature. |
| Thermopile | Temperature | Works on the principle of the Seeback effect. Thermal energy is converted into emf. |
| Piezo electric pickup | Sound, Vibration, Acceleration & Pressure | An emf is generated when an external force is applied to crystal materials such as quartz. |
| Photovoltaic transducer | Solar cell, Light Meter | An emf is generated in a semiconductor junction device when light radiation falls on the device. |
PASSIVE TRANSDUCER
What is meant by Passive Transducer?
The transducer which requires external energy to produce its output is called a passive transducer. This transducer requires external energy to process the output from the sensing element to produce respective electric output. The electrical parameters in a passive transducer are resistance, inductance, and capacitance which require external energy for conversion.
Block Diagram of Passive TransducerThe block diagram of a passive transducer shown above has external energy. This passive transducer consists of a sensing element and a transduction element. The pressure, temperature, stress and displacement are the various input that can be measured.
Sensing element like RTD, strain gauge and LVDT is used to measure temperature, applied force and displacement respectively. This sensing element is used for sensing the change in input quantity which is to be measured and convert the physical change into the electrical property such as resistance, inductance & capacitance change. This is fed to the transduction element.
What is the key difference between active and passive transducer?
In an active transducer, the energy required for its operation is taken from the quantity that has to be measured but in passive transducer energy needed for operation is derived from an external source.
Passive Transducer Classification
Passive transducer is classified based on the transduction medium. They are listed below.
- Variable reactance [capacitance & inductance] based passive transducer
- Optoelectronics based passive transducer
| Passive transducer | Electrical Parameter | Parameter to Measure | Principle of operation |
| Potentiometric transducer | Resistance | Pressure, Displacement | When an external force varies the slider position of the potentiometer, then the resistance varies in the bridge circuit. |
| Resistance thermometer (RTD) | Resistance | Temperature, Heat radiant | Resistance of pure metal wire with a large positive coefficient of resistance varies with temperature. |
| Thermistor | Resistance | Temperature | Resistance of certain metal oxides with a negative temperature coefficient of resistance varies with temperature. |
| Strain gauge | Resistance | Applied Force, Pressure, Torque, Displacement | When stress is applied there is a change in the resistance of the wire by elongation or compression. |
| Hot wire meter | Resistance | Gas flow, Gas pressure | Resistance of a heating element is varied by convection cooling of a stream of gas |
| Photoconductive cell | Resistance. | Photosensitive Relay | Resistance of the cell as a circuit element varies with incident light. |
| Resistance hygrometer | Resistance | Relative humidity | Resistance of conductive strip changes with moisture content. |
| Capacitor microphone | Capacitance | Sound | Sound pressure varies between a fixed plate and a movable diaphragm. |
| Reluctance pick up | Inductance | Pressure, Vibration, Displacement & Position | When changing the position of the iron core of the coil, the reluctance of magnetic circuits is varied. |
| LVDT | Inductance | Pressure, Force, Displacement, Position | When there is a change in displacement there is a change in inductance. |
ACTIVE TRANSDUCER VS PASSIVE TRANSDUCER
Difference between Active & Passive Transducer
| Parameter | Active Transducer | Passive Transducer |
| Principle | The quantity being measured provides operational energy. | Energy for operation is taken from an external source. |
| Other name | Self-generating transducer | Externally driven transducer |
| Type of output | Electrical current or Voltage | Changes in quantity associated with passive elements is observed. |
| Conversion technique | Simple | Complex |
| External Energy | Not required | Required |
| Amplification | Needed | Not Required |
| Resolution | Low | High |
| Example | Thermocouple, Piezoelectric crystal, etc. | Potentiometer, Thermistor, Differential Transformer, Photovoltaic cell, etc. |
List some advantages & disadvantages of Active transducer & Passive transducer
The below table shows advantages and disadvantages of some active and passive transducer based on transduction mechanism.
ACTIVE TRANSDUCER
| Transduction Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Thermocouple | 1.Available in a compact dimension 2. Rapid temperature response 3. No need for a bridge circuit | 1. Nonlinear 2. Hard to re-calibrate 3. Reference junction at cold temperature |
| Piezoelectric | 1. Excellent Spatial Resolution 2. Precise sensitive 3. Not dependent on temperature. | 1. Lack of spatial resolution 2. Charge related leaks present 3. Rely on dynamic sensing |
PASSIVE TRANSDUCER
| Transduction Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Capacitive type transducer | 1. High sensitivity 2. High Spatial resolution 3. Large dynamic range 4. Temperature independent | 1. Difficult measuring circuit 2. Stray capacitances 3. Cross-talk between parts of elements 4. Vulnerable to noise |
| Inductive type transducer | 1. Output is linear 2. Sensitivity is high 3. Power output is high 4. Dynamic range]s high | 1. Low frequency response 2. Unreliable 3. Higher Energy consumption |
| RTD | 1. Stability is high 2. Most precise output is obtained when compared to 3. thermistor 4. Excellent repeatability | 1. High cost 2. Complex circuit design 3. Current source required |


